|
P
P | Q
parabola
a conic section; specifically, the shape formed by the graph of the function y = x2 or the relation x = y2
The parabola is probably the most famous conic section because we see it in real life: in the shape of bowls, in the path of a ball thrown through the air as gravity takes over and sends the ball back down to earth, in the shape of telescope
mirrors.
parallel ( ) )
two lines that are everywhere the same distance apart and never intersect
We use the symbol  for parallel lines. If AB and CD are two parallel line segments, we say AB
for parallel lines. If AB and CD are two parallel line segments, we say AB
 CD. CD.
parallelogram
a quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite sides are parallel
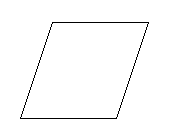
The above figure is a parallelogram. All rectangles and squares fall under this class of quadrilaterals; they are special types of parallelograms.
parallels
the east-west imaginary lines on a globe parallel to the equator; the lines that measure latitude on a world map
parentheses [ ( ) ]
symbols ( ) that show grouping or multiplication
If the parentheses have an operation symbol ( +, -, etc.) inside them in addition to
numbers and variables, they are being used as grouping symbols. According to the order of operations agreement, whatever appears inside the parentheses should be done first.
If the parentheses simply separate one number from another number, as in the example 6(4), the parentheses mean you should multiply the two numbers.
pattern
any set (numbers, figures, etc.) that seems to be in a certain order, from which you could predict the next element in the set; a sequence of numbers of items that continue according to a rule
pentagon
a polygon with five sides and five angles
per
for one thing – a clue word for division
Prices in stores are often stated using per. For example, peaches may cost $1 per pound. We also use per in measuring rates of speed. For example, speed is distance over time, so we measure it as miles per hour or meters per second.
percent (%)
parts per 100; the numerator of a fraction with denominator 100
The symbol for percent is %.
percent (of) decrease
a decrease of a quantity expressed as a portion of its original value
To find the percent of decrease between two numbers, first find the difference between the two numbers. Then write a fraction with the difference as the numerator and the ORIGINAL AMOUNT (the larger of the two numbers) as the denominator. Then divide the fraction to get a decimal and finally convert the decimal to a percent. This is the percent of decrease.
percent (of) increase
an increase of a quantity expressed as a portion of its original value
To find the percent of increase between two numbers, first find the difference between the two numbers. Then write a fraction with the difference as the numerator and the ORIGINAL AMOUNT (the smaller of the two numbers) as the denominator. Then divide the fraction to get a decimal and finally convert the decimal to a percent. This is the percent of increase.
percent statement
a formula that helps solve percentage problems: The percent times the whole equals the part.
perfect number
a counting number that equals the sum of its factors except itself
The first three perfect numbers are 6, 28, and 496.
perimeter of a polygon (usually abbreviated as P in formulas)
the sum of the lengths of the sides of a polygon; the distance around a plane figure
period
in a number written in standard form, each group of three digits separated by a comma
For example, the number 234,567,890 has three periods.
perpendicular ( ) )
intersecting at right angles
Both lines and planes can be perpendicular. We use the symbol  to show that lines or planes are perpendicular.
to show that lines or planes are perpendicular.
pi (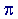 ) )
the ratio of the circumference to the diameter of a circle
Pi is a constant, approximately equal to 3.1416 or 22/7. Pi is an irrational number, a nonterminating decimal.
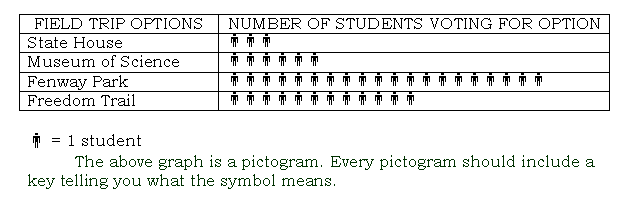
pictograph
a graph that uses symbols to represent data
pint (pt.)
a US customary measure of capacity equal to 2 cups or ½ quart
place value
the idea that the position of each digit in a number in standard form determines how much that digit is really worth
For example, in the number 528,000, the digit 5 is in the hundred thousands place, so the 5 doesn’t mean 5, it means 5 hundred thousand (500,000).
The places values for whole numbers, in order from right to left starting at the decimal point, are:

There is no largest number, so there is no largest place value. However, we tend to use scientific notation to write large numbers.
The decimal part of decimal numbers use the idea of place value, too. The place values for decimals, in order from LEFT TO RIGHT starting at the decimal point, are:

Note that if you think of the units place and the decimal point as being the “middle” of a number, all other place values are symmetrical – tens to the left of the units place, tenths to the right; hundreds two places to the left of the units place, hundredths two place to the right, etc.
plane
a flat surface; a two-dimensional surface
plane figure/two-dimensional figure
a figure that lies totally in a plane
Plane figures include all polygons and circles.
plot a graph
to create a graph of an equation by placing dots where solutions of that equation are found on a coordinate system
plus sign (+)
the symbol (+) that shows addition
points
a term banks use to mean percent of a mortgage; used to express the loan origination fee
polygon
a closed figure made up of line segments that intersect only at their end points; a plane figure that uses only straight lines
polyhedron
a three-dimensional figure in which each face is a polygon, and the polygons only intersect at the edges
Examples of polyhedrons include cubes, dodecahedrons, icosahedrons, prisms, pyramids, and tetrahedrons.
population
a large group of people, places, or things about which information is being gathered
With many scientific and social science studies, it is highly impractical to gather
information about an entire population. Instead, the researchers use a sample of the population. They spend a good deal of effort making sure that the sample is random and representative of the population as a whole, in order that they can generalize about the population based on their results with the sample.
positive numbers
numbers that are to the right of 0 on a number line
pound (lb.)
a US customary unit of weight equal to 16 ounces
power
(1) a number indicating repeated multiplication; (2) the rate at which work is done or energy released
When a number (the base) is raised to a power (the exponent), it means that you have a special type of multiplication problem. The base is the only number that appears in your problem.
The exponent tells you the number of times you write the base number in your problem (connected by multiplication symbols). For example, 34 has a base of 3 and an exponent of 4. That means I have a multiplication problem in which the number 3 appears 4 times: 3 x 3 x 3 x 3 = 81. So 34 = 81.
prime factorization form
a number expressed as a unique product of prime factors, usually multiplied in order from least to greatest
The fundamental theorem of arithmetic is that there is one and only one way to write any number in prime factorization form.
prime number
a natural number greater than 1 and with only two factors, 1 and itself
The prime numbers less than 50 are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, and 47.
A very simple use for prime numbers is to help you decide if a fraction is in lowest terms.
A fraction that has prime numbers as its numerator and denominator with the smaller of the two prime numbers as the numerator is automatically in lowest terms. Fractions like 2/3, 5/11, and 3/23 are all in lowest terms.
A far more sophisticated use of prime numbers is in cryptography, code making.
Encryption is important in computer security and in espionage.
principal
the amount of money originally deposited or borrowed; sometimes known simply as “the amount”
prism
a polyhedron with two congruent parallel bases; a polyhedron that consists of figures that have a pair of opposite sides that are parallel; a polyhedron that keeps its shape for its entire length

probability
the ratio of the number of favorable outcomes to the number of possible outcomes; a number between 0 and 1 that describes the likelihood that an event will occur
Probability is sometimes written as P. If you are speaking of probability and note P =1, you mean that you have a sure thing: that something must happen; nothing else can happen.
The probability that an event will happen is equal to the number of ways the event can happen over the number of possible outcomes, provided that the possible outcomes are equally likely. For example, say that I have 5 marbles in a bag, 2 of them red and 3 of them blue. The probability that I will draw a blue marble out of the bag (that’s the event I want to happen) is 3 out of 5 (or 3/5), because the numbers of ways I can draw a blue marble is 3 (there are 3 blue marbles in the bag), and the number of possible outcomes is 5 (there are 5 marbles total in the bag).
product
in multiplication, the result of multiplying two numbers; the answer to a multiplication problem
proper factors
all the factors of a number, except the number itself
proper fraction
a fraction less than 1; a fraction whose numerator is less than its denominator
An improper fraction is never in lowest terms. A proper fraction may or may not be in lowest terms.
properties of shapes
characteristics of shapes that are always valid
Properties of shapes include things like the number of sides, the number of angles, length, width, height, area, perimeter, and volume.
proportion
an equation stating that two ratios are equal
If you choose to write a proportion using fraction notation, each ratio is one fraction, and the two fractions are equivalent. For example, ½ is proportional to 4/8 because ½ = 4/8.
You can also use the : and :: symbols to show ratios and proportions. For example, we can write 1:2::4:8 to show the previous example. We would read this, “one is to two as four is to eight.”
protractor
an instrument used to measure angles
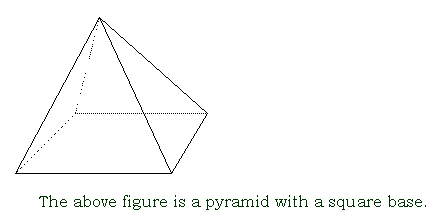
pyramid
a polyhedron with one base that is a polygon and several lateral faces that are triangles meeting at a vertex
Pythagorean theorem
in any right triangle, the square of the first leg plus the square of the second leg equals the square of the hypotenuse
Formally stated: For any right triangle with legs a and b and hypotenuse c, a2 + b2 = c2.
top
Q
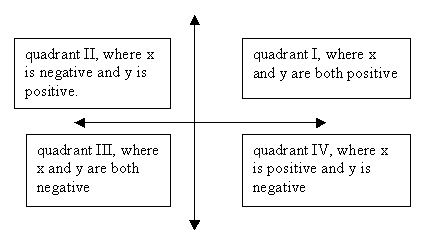
quadrants
the four regions in a rectangular coordinate system
quadratic equation
an equation in one variable for which at least one term involves the square of the variable but never any higher powers of the variable
The general form of a quadratic equation is ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a ¹ 0.
quadratic formula
a formula that helps you help the solutions (if they exist) of a quadratic equation
Specifically, for a quadratic equation written in the general form ax2 + bx + c = 0, the solutions can be found by substituting the appropriate values for a, b, and c into the following formula:
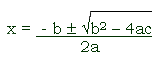
quadrilateral
a polygon with four sides and four angles with sum 360°
quart (qt.)
a US customary measure of capacity equal to ¼ gallon
quotient
the answer to a division problem
back to top
|