|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A
Glossary of Math Terms
A-B |
C | D-F |
G-L | M-O | P-Q | R |
S | T-Z
|
gallon (gal.) H height (usually abbreviated h in formulas)how tall something is; the "vertical" measurement height of a triangle (usually abbreviated h in formulas) a line drawn perpendicular to the base of a triangle; the same as altitude of a triangle hemisphere a half of a sphere, made by cutting the sphere along a plane that contains the center point of the sphere heptagon a polygon with seven sides hexagon a polygon with six sides horizontal running left to right; running parallel to the skyline of a calm ocean horsepower (hp) a US customary unit of power. 1 horsepower = 500 foot-pounds-per-second hour (h.) a unit of time equal to 60 minutes; the amount of time it takes the earth to rotate 15° hourly every hour hourly wage the rate of pay for each hour worked Contrast this with salary, which offers an annual, monthly, biweekly or weekly amount no matter how many hours are worked. hyperbola a type of conic section; the curve made by the section of a cone that has been cut at an angle more steeply inclined to the base than the side of a cone hypotenuse in a right triangle, the side opposite the right angle 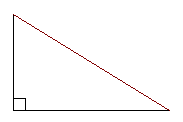
In the above right triangle, the hypotenuse is the side marked in red. The hypotenuse does not help form the right angle of the triangle; it is opposite the right angle. top I icosahedrona solid with twenty faces If the icosahedron is regular, the twenty faces will be equilateral triangles. identical exactly the same shape and size; congruent identity element for an operation an element which doesn’t does change other elements when tit is combined with them under a certain operation The identity element for addition is 0 because when you add 0 to any number, you don’t change the value of the original number. The identity element for multiplication is 1, because when you mutliply any number by 1, you don’t change the value of the original number.Set have identity elements for their operations, too. For the operation called union, the identity element is f, the null set. A È f = A. For the operation called intersection, the identity element is the universal set. B Ç the universal set = B. identity mapping a mapping in which each element maps onto itself The line y = x is an identity mapping. image the result when a number is mapped; the result when an object is transformed; an element of the range of a function improper fraction a fraction whose numerator is greater than its denominator; a fraction that can be reduced to an integer or mixed number inch (in. or ”) a US customary unit of length equal to 1/12 foot increase to make a number larger independent variable one of the variables in a relationship, the one whose value determines the value of the other (dependent) variable inequality a statement that two quantities are not equal We use the symbol infinite set a set with an infinite, or endless, number of members We cannot list every member of an infinite set, because our list would never end. Instead, we write a few of the members of the set, just enough to tell what the pattern is, what the rule is for going from the first member to the second, etc., and then we use the ellipsis punctuation marks (…) to show that the set follows that same rule forever. For example, {even numbers} = {2, 4, 6,…} input for a function, the value substituted for the independent variable integers the set I = {…,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,…} intercept the point where the graph of an equation crosses an axis interest the amount of money paid for the privilege of using someone else's money interest rate the percent used to determine the amount of interest intersecting lines and curves lines or curves in a plane that cross or touch If I graph two lines and they intersect at a point, that point will be a solution to both equations. intersection of two sets the set that contains all common elements of two given sets If the two sets have the empty set as their intersection, it means they have no elements in common. In a Venn diagram, we show that there is an intersection between two sets by drawing two overlapping circles. The part that overlaps is the intersection. invariants properties of an object and an image that are the same before an after a transformation For example, I can rotate a shape 90° but that transformation doesn’t change the area of the shape, so area would be an invariant. inverse operations operations that reverse the effect of each other, like addition and subtraction or multiplication and division inverting a fraction interchanging the numerator and the denominator of a fraction irrational numbers numbers that cannot be expressed as the ratio of two integers Examples of irrational numbers are pi and the square root of 2. When expressed in decimal notation, irrational numbers are non-terminating decimals. isometries transformations which do not change the length of the figures being transformed Rotation, reflections and translations (turns, flips, and slides) are isometric transformations. Shapes that have been rotated, reflected or translated keep the same dimensions. isosceles trapezoid a trapezoid in which the nonparallel sides are congruent isosceles triangle a triangle with two sides of equal length In an isosceles triangle, two angles will be of equal measure, too. top K Kelvin (° K.)a scale of temperature measured in degrees Celsius from absolute zero (-273.15° Celsius) kilo- a prefix that indicates 1000 units kilogram (kg.) a unit of mass equal to 1000 grams kilometer (km.) a unit of distance equal to 1000 meters kite a quadrilateral that has two pairs of congruent adjacent sides. 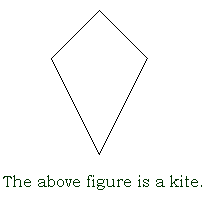
top L lateral areathe area of the surfaces, other than bases, of a prism, pyramid, cylinder, or cone lateral faces the faces of a prism or pyramid that are not bases latitude the number that measures how far north or south one is of the equator; the horizontal lines on a map; lines parallel to the equator on a world map leading zero a zero that is the only digit before a decimal point The leading zero can be dropped without changing the value of a number. (0.1 = .1) You can add as many leading zeroes as you like to a decimal number. This is useful to do before dividing a decimal number by a power of ten. For example, if I have the number .45 and I want to divide it by 100, I would start by adding leading zeroes to make the number 00.45. Then I can divide by 100 simply by moving the decimal point two places to the left. So .45 divided by 100 = .0045. least smallest least common denominator (LCD) the least common multiple of the denominators of the fractions being compared least common multiple (LCM) the smallest number other than zero that is a multiple of two or more numbers For example, the multiples of 2 are {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12,…}. The multiples of 5 are {5, 10, 15, 20, 25,…}. The smallest number that is both a multiple of 2 and a multiple of 5 is the number 10, so 10 is the least common multiple of 2 and 5. legs in a right triangle, the sides that form the right angle less than (<) appearing to the left of a given number on the number line like fractions fractions that have the same denominator like terms terms that have the same variable raised to the same power Like terms in an equation or an expression can be combined. For example, the expression 4 a + 5 b + 2a –3a can be simplified as combining like terms to 3a + 5b. line a straight path of points that extend indefinitely in opposite directions line graph a graph that displays data as points that are connected by segments 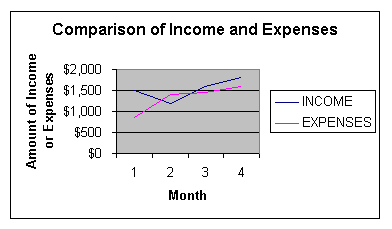
The above figure is a line graph that compares two variables (income and expenses) over time. line of symmetry a line that divides a figure into two halves that are mirror images of each other A figure may have more than one line of symmetry or it may have none at all. line segment the shortest distance between two points; two points on a line, plus all the points in between. The two points are called the endpoints of the segment. linear equation an equation for which the graph is a line Linear equations can be written in the form y = ax + b, where a is the slope of the line and b is the y-intercept. linear measurement a measure of length or distance linear relationship a relationship in which there is a constant rate of change between the two variables; for each unit increase in one variable, there is a constant change in the other variable liter (l.) the basic metric unit of volume (capacity) equal to 1,000 cubic centimeters locus the line, or path, of a set of points that follow some rule A circle is a locus. The rule for making a circle is to take two points and allow the line segment between them to be the radius of the circle. Keep one point fixed as the center point of the circle, but rotate the other point 360°. The path of points equidistant from the center point becomes the circle. longitude the number that measures how far east or west one is from the zero, or prime, meridian; the lines that run vertically on some world maps; the curved lines that run from the north to the south pole on some maps lowest terms describing fractions that are not able to be reduced; simplest form See simplest form for further details. |